BLOG
Addressing AI Cybersecurity Risks in Healthcare Organizations
Published On November 8, 2023
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)[1] provides a wealth of information on cybersecurity and provides several frameworks considered the gold standard in risk management.
As artificial intelligence (AI) continues to be integrated into various industries, its potential benefits and risks are becoming increasingly apparent. In the healthcare sector, AI has the potential to revolutionize patient care and improve overall efficiency. However, with this increased use of AI comes the need for stricter cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive patient data.
In anticipation of new cybersecurity risks introduced by artificial intelligence (AI), NIST launched a new AI Risk Management Framework (RMF)[2].
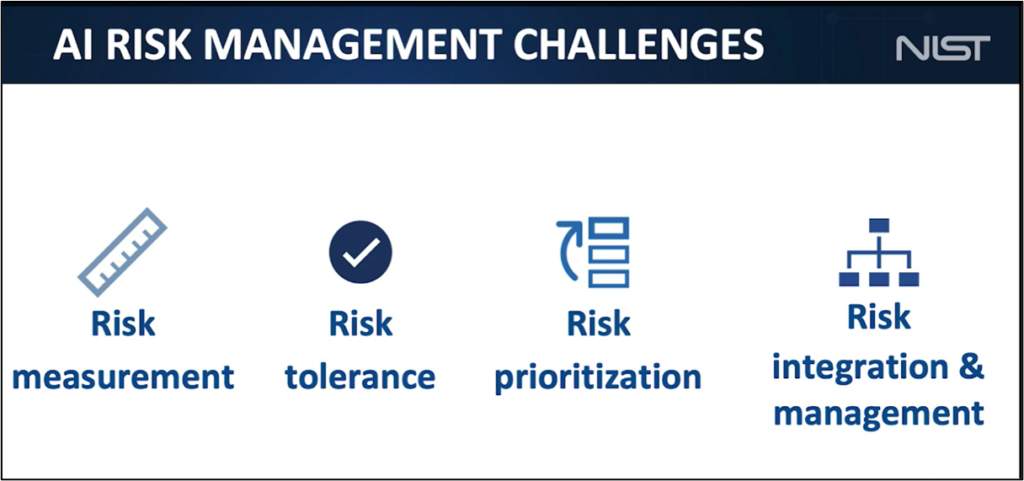
The AI RMF addresses AI risk management challenges:
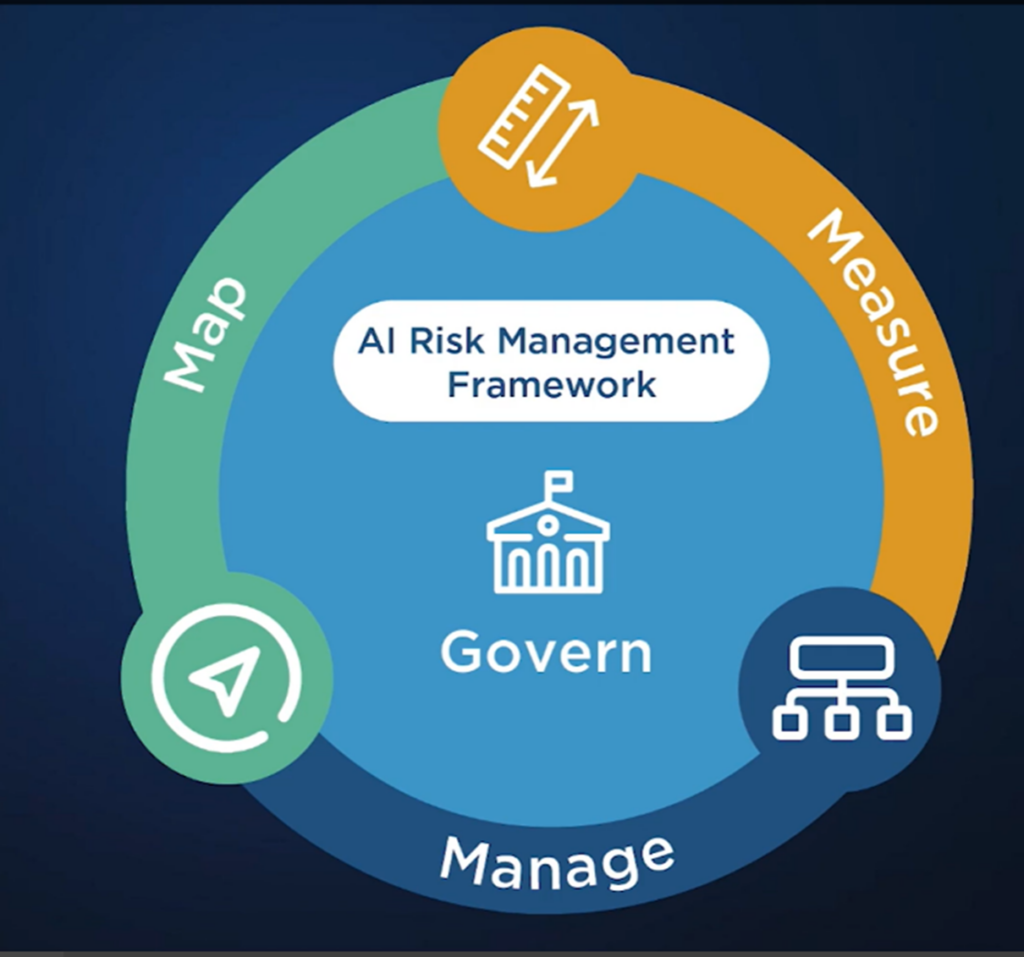
The AI RMF consists of four functions:
The four functions are broken down into 19 categories and 72 subcategories.
I know, you’re thinking, not another framework to figure out. The good news is that NIST provides a comprehensive companion playbook[3] written in plain English, not NIST-speak, to help organizations navigate the AI RMF. Suggested tactical actions and extensive references guide each organization to apply the RMF within their own contexts.
Without proper risk management, AI can introduce vulnerabilities and threats to health care organizations. As technology continues to advance, the integration of AI into healthcare systems is inevitable. However, this also means that the potential for cyberattacks and data breaches increases.
The NIST AI RMF serves as a guide for health care organizations to identify, assess, and manage cybersecurity risks.
NIST provides an online version of the playbook[4] that is interactive so you can drill down to the controls that are of interest without reading the whole playbook.
NIST also recommends establishing Governance and then tackling Map before moving on to Measure and then Manage rather than trying to do it all once.
So what exactly do the four functions look like?
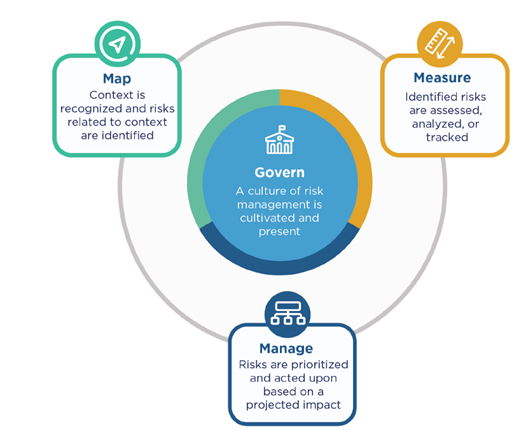
GOVERN enables the other functions of the framework by facilitating an organizational culture of risk. Senior leadership sets the tone for risk management within an organization, and with it, organizational culture.
MAP establishes the context to frame risks related to an AI system. The information gathered while carrying out the MAP function enables negative risk prevention and informs decisions for processes such as model management, as well as an initial decision about appropriateness or the need for an AI solution.
Outcomes of the MAP function are the basis for the MEASURE and MANAGE functions. Without contextual knowledge, and awareness of risks within the identified contexts, risk management is difficult to perform. The MAP function is intended to enhance an organization’s ability to identify risks and broader contributing factors.
MEASURE employs quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method tools, techniques, and methodologies to analyze, assess, benchmark, and monitor AI risk and related impacts. Measure uses knowledge relevant to AI risks identified in the MAP function and informs the MANAGE function.
Measuring AI risks includes tracking metrics for trustworthy characteristics, social impact, and human-AI configurations. Where tradeoffs among the trustworthy characteristics arise, measurement provides a traceable basis to inform management decisions.
Measurement outcomes will be utilized in the MANAGE function to assist risk monitoring and response efforts.
MANAGE allocates risk resources to mapped and measured risks as defined by the GOVERN function. Risk treatment comprises plans to respond to, recover from, and communicate about incidents or events.
Contextual information gleaned from expert consultation and input from relevant AI actors established in GOVERN and carried out in MAP is utilized in this function to decrease the likelihood of system failures and negative impacts. Processes for assessing emergent risks are in place, along with mechanisms for continual improvement.
After completing the MANAGE function, plans for prioritizing risk and regular monitoring and improvement will be in place. Framework users will have enhanced capacity to manage the risks of deployed AI systems and to allocate risk management resources based on assessed and prioritized risks. It is incumbent on Framework users to continue to apply the MANAGE function to deployed AI systems as methods, contexts, risks, and needs or expectations from relevant AI actors evolve over time.
HITRUST CSF v11.2.0[5] now includes mappings to NIST AI RMF v1.0, ISO/IEC 23984, and ISO 31000. These new authoritative sources can be included in your HITRUST r2 assessment by selecting the new Compliance Factor "Artificial Intelligence Risk Management".
ISO now includes two new guides on AI and risk management. ISO/IEC 23894:2023 "Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Guidance on risk management"[6] provides guidance on how organizations that develop, produce, deploy or use products, systems and services that utilize AI can manage risk specifically related to AI. The guidance also describes processes for the effective implementation and integration of AI risk management.
The ISO 31000 "Risk Management framework"[7] has also been updated to include AI.
As a certified HITRUST external assessor, Meditology can assist with your HITRUST v11.2 assessment. We also plan to incorporate AI as a domain within our traditional security risk assessments (SRAs). We are also developing a new SRA specific AI and will be able to assist you in determining your compliance with NIST AI RMF.
We are here to assist you with your journey in AI risk management.
Interested in learning more? Sign up for our webinar where we will take a deep dive into the AI RMF framework.
About the Author
MALIHA CHARANIA, MSIS, MSCS, HITRUST | DIRECTOR, IT RISK MANAGEMENT
Maliha serves as the leader of Risk Advisory Services. She has designed, led, and implemented numerous global IT security and risk management initiatives in both healthcare and academia. Maliha has over 14 years of experience with extensive technical security knowledge and has served as a Subject Matter Expert in matters of IT security and compliance for many healthcare providers, business associates, and payers of varying sizes and across the world. Maliha has extensive knowledge in various standards and legislation including HIPAA, GDPR, ISO, NIST, and HITRUST. Maliha’s combination of consulting and hands-on experience at an international level is what distinguishes her in the IT Risk Management and Cybersecurity field.
https://www.linkedin.com/in/maliha-charania/
Resources
[1] https://www.nist.gov/
[2] https://airc.nist.gov/AI_RMF_Knowledge_Base/AI_RMF
[3] https://www.nist.gov/itl/ai-risk-management-framework/nist-ai-rmf-playbook
[4] https://airc.nist.gov/AI_RMF_Knowledge_Base/Playbook
[5] https://hitrustalliance.net/
[6] https://www.iso.org/standard/77304.html
[7] https://www.iso.org/iso-31000-risk-management.html/